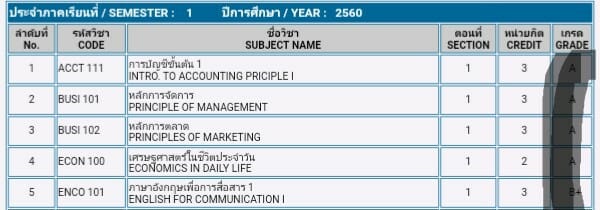
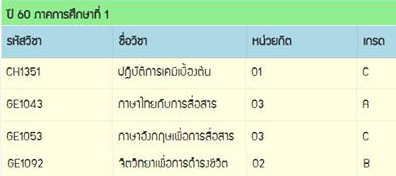
เรือ 2 ลำ กับเรือที่ไม่ได้เรื่อง
เรือ 2 ลำ กับเรือที่ไม่ได้เรื่อง
หลังอ่านนิทานของ อ.ชีวิน สุนสะธรรม
เรื่อง “เรือที่ไม่ได้เรื่อง” ทำให้นึกถึง
TQF = กรอบมาตรฐานคุณวุฒิระดับอุดมศึกษาแห่งชาติ
ที่กำหนดว่าทุกหลักสูตรต้องสอนเรื่องคุณธรรมจริยธรรม
โดยแทรก คุณธรรม จริยธรรม (Morality and Ethics) เข้าไปในทุกรายวิชา (มคอ.3)
1) ตระหนักในคุณค่าและคุณธรรม จริยธรรม เสียสละ และซื่อสัตย์สุจริต
2) มีวินัย ตรงต่อเวลา และความรับผิดชอบต่อตนเองและสังคม
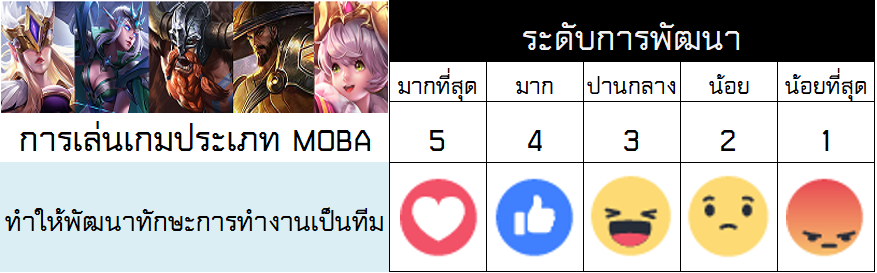
3) มีภาวะความเป็นผู้นำและผู้ตาม สามารถทำงานเป็นทีมและสามารถแก้ไขข้อขัดแย้งและลำดับความสำคัญ
4) เคารพสิทธิและรับฟังความคิดเห็นของผู้อื่น รวมทั้งเคารพในคุณค่าและศักดิ์ศรีของความเป็นมนุษย์
5) เคารพกฎระเบียบและข้อบังคับต่าง ๆ ขององค์กรและสังคม
6) สามารถวิเคราะห์ผลกระทบจากการใช้คอมพิวเตอร์ต่อบุคคลองค์กรและสังคม
7) มีจรรยาบรรณทางวิชาการและวิชาชีพ
จากนิทานด้านล่าง ทำให้นึกถึงสุภาษิตคำพังเพยว่า
“ถ่มน้ำลายรดฟ้า” และ
“ความผิดคนอื่นเท่าภูเขา ความผิดของเราเท่าเส้นผม”
เรื่อง เรือที่ไม่ได้เรื่อง โดย ชีวิน สุนสะธรรม
https://www.facebook.com/cheevin.soonsatham
กาลครั้งหนึ่งเมื่อไม่กี่ปีมานี้ มีชายขับเรือคนหนึ่ง
ได้ประกอบเรือขึ้นมา 1 ลำ มันไม่ใหญ่อะไรมาก
แต่หวังว่าจะสามารถส่งผู้โดยสารให้ไปถึงอีกฝั่งหนึ่งได้
และใครที่จะไปขึ้นอีกฝั่งนึงได้
จะต้องมีปลามากมายที่จะต้องตกให้ได้ระหว่างทาง
ชายขับเรือมองเห็นชายหนุ่มผู้หนึ่งที่มีความสามารถในการตกปลา
จึงเดินไปบอกกับเขาว่า
“ไอ้หนุ่ม .. มาขึ้นเรือของฉันไหม
ฉันจะให้เธอขึ้นฟรีฟรีเลย
เพราะฉันเห็นว่าเธอจะตกปลาได้มากมาย
และพอไปถึงฝั่งนู้น เรือของฉันจะได้เป็นที่รู้จัก”
หนุ่มคนนั้นก็เลยยอมที่จะขึ้นเรือลำเล็ก ๆ
และไปพร้อมกับชายขับเรือ
ระหว่างทาง หนุ่มตกปลาได้รับการสอนเทคนิค
ในการตกปลา เพื่อให้จับปลาให้ได้มากขึ้นจากชายขับเรือ
แต่ยังไงก็ตาม หนุ่มตกปลาก็เฝ้ามองแต่เรือลำใหญ่ที่อยู่ข้าง ๆ
และชื่นชมเรือลำใหญ่นั้นว่าสะดวกสบาย
ชายขับเรือเห็นเช่นนั้น
จึงพยายามทำทุกอย่างที่จะทำได้
ให้เหมือนกับเรือลำใหญ่
ไม่ว่าจะพาชายหนุ่มตกปลาในที่ปลาชุกชุม
เพื่อให้ตกปลาได้มากขึ้น
และพยายามเอาใจใส่ดูแลใกล้ชิดอย่างเต็มกำลัง
ให้ได้มากกว่าบรรดาผู้โดยสารในเรือลำใหญ่จะได้รับเสียด้วยซ้ำ
แต่ถึงพยายามเพียงใดก็ตาม ด้วยความเป็นเรือใหม่
จึงมีข้อบกพร่องต่าง ๆ บ้าง
แต่ชายหนุ่มก็ไม่เห็นถึงความพยายาม
ทำดีที่สุดของคนขับเรือเพื่อให้ชายหนุ่มตกปลา
ได้ปลาเยอะที่สุดก่อนที่จะถึงฝั่ง
ชายหนุ่มตกปลาไม่สนใจว่าตัวเองได้ปลามามากแค่ไหน
และไม่สนใจว่าคนขับเรือจะดูแลเอาใจใส่มากน้อยเพียงใด
แต่ก็ยังรู้สึกหงุดหงิดที่เรือลำนี้มันไม่สบาย “มันไม่ได้เรื่อง”
เมื่อถึงฝั่ง ชายหนุ่มตกปลาเดินขึ้นฝั่งพร้อมปลามากมาย
และประกาศให้ทุกคนรับทราบว่า “เรือลำนี้ไม่ได้เรื่อง”
แต่ก็มีผู้คนถามมาว่า
“ถ้าเรือลำนี้ไม่ได้เรื่องแล้ว เจ้าได้ปลามาจากไหนมากมาย”
ชายหนุ่มบอกว่า “มันเป็นความสามารถของข้าเอง แต่เรือมันไม่ได้เรื่อง”
และก็มีคนถามว่า “แล้วคนขับเรือล่ะ ดีไหม”
ชายหนุ่มก็ตอบว่า “คนขับเรือก็ดี แต่ช่างเถอะ เรือมันไม่ได้เรื่อง”
ทุกคนจึงรับทราบและจดจำกันไปว่า
เรือของชายหนุ่มคนนี้นั่งมา “มันไม่ได้เรื่อง”
หลังจากนั้น ไม่ว่าชายหนุ่มคนนี้เอาปลาไปขายที่ไหน
ทุกคนก็จะรู้ว่า เป็นชายหนุ่มคนที่นั่งมากับเรือที่ไม่ได้เรื่อง
ในที่สุด
ชายหนุ่มมีเงินมากมายจากการขายปลาที่ตัวเองตกมาได้
และพยายามไม่บอกใคร ว่าตัวเองนั่งเรืออะไรมาจนถึงฝั่ง
เพราะยังไง “เรือมันก็ไม่ได้เรื่อง”
คำถามท้ายนิทาน
“นิทานเรื่องนี้สอนให้รู้ว่า .. อะไร”
ล่องแพเหนือเขื่อนกิ่วลม 2559 เล่าด้วย 4 ภาพ